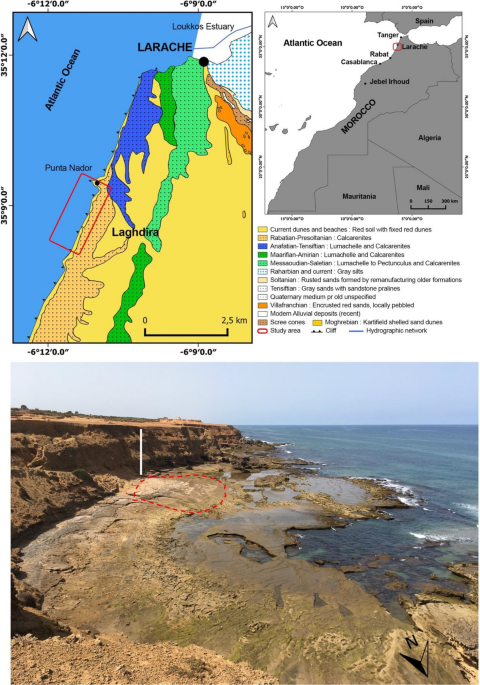
A Late Pleistocene hominin footprint site on the North African coast of Morocco
The discovery of the Larache footprints represents further evidence of the importance of North Africa, and the Moroccan region in particular, during hominin evolution. The western Atlantic coast between Rabat and Tangier, where the Larache footprints are located, was occupied in several places. From an ichnological point of view, the Larache footprints represent an important discovery. While Pleistocene Homo sapiens were hunter-gatherers, individuals likely left the Larache footprints while probably searching for resources. In this context, the preferential orientation of the Larache footprints towards the offshore could maybe indicate the search for marine resources.
Source: The North Africa Journal January 23, 2024 08:12 UTC




