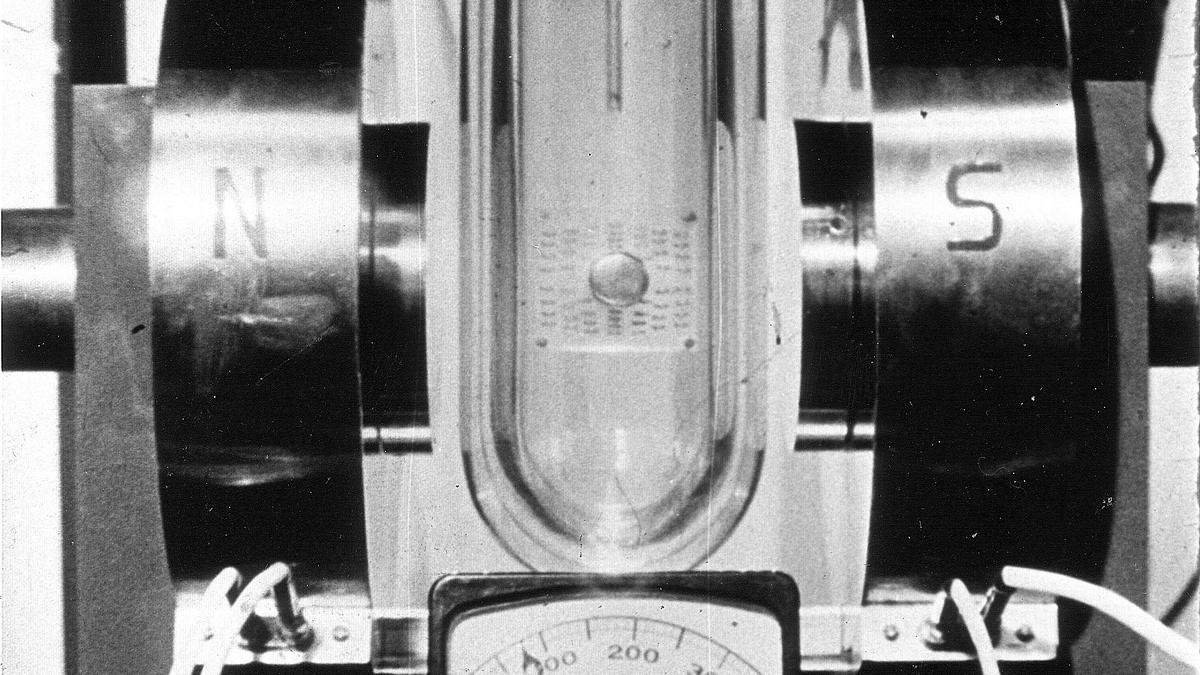
How to check if a material is a superconductor – in four steps
When a material becomes a superconductor, the superconducting state will induce four changes in the material. This is the Meissner effect: a magnet placed near the material will be pushed away as the material transitions to a superconducting state. As the material transitions to its superconducting state, the electronic specific heat drops. Upon warming the material back up to the critical temperature (below which the material is a superconductor), it jumps back to the value it was when the material was not superconducting. 4: Spectroscopic effect – The electrons in the material are forbidden from attaining certain energy levels, even if they could when the material wasn’t a superconductor.
Source: The Hindu August 07, 2023 12:14 UTC







